Large-scale energy storage innovators roll out safer, smarter, more scalable systems in September
From AI-optimized microgrids to next-gen high-density storage and new C&I battery systems, companies including Eaton, Schneider, Viridi, Wärtsilä, Delta, and Fluence unveiled advances that target resilience, safety, and cost savings across the clean energy landscape

The energy storage and microgrid sector is moving fast on three fronts: embedding AI to cut costs and improve performance, engineering new safety systems to prevent high-profile battery fires, and scaling hardware to serve everything from grocery stores to hyperscale data centers. To see what we mean, here are seven intriguing announcements since RE+ 2025 that spotlight new technologies and partnerships that will make an impact larger-scale battery energy storage system deployments in 2026.
Eaton and Xendee: AI modeling meets hardware integration
Eaton is putting capital and expertise behind Xendee, the microgrid design and operations platform, through a new Series B financing round and a formal collaboration. The goal is to marry Eaton’s power management hardware with Xendee’s AI-driven Model Predictive Control software to create an integrated solution for both new and existing microgrids.
Xendee’s platform allows operators to model and optimize more than 27 different DER technologies, including solar, batteries, CHP, linear generators, nuclear, and even hydrogen fuel cells. Its AI engine continuously evaluates forecasted scenarios to adjust system dispatch in real time. By integrating this with Eaton’s switchgear, distribution gear, and engineering services, project owners gain a single pathway from design to operation.
“Together with Xendee, we’re unlocking new ways to help customers maximize the functionality and value of their microgrid investments,” said Angie McMillin, president of Energy Solutions and Services at Eaton.
For customers, that means microgrids capable of dynamically shifting loads and generation sources to cut operating costs, extend equipment life, and boost resilience. The solution is hardware-agnostic but packaged as a turnkey option—a rare combination in the fragmented microgrid market. Expect to see this pairing deployed first in North America and Europe, where policy drivers and rising electricity demand are fueling investment in flexible grid assets.
Sungrow: PowerTitan 3.0 pushes liquid-cooled storage forward
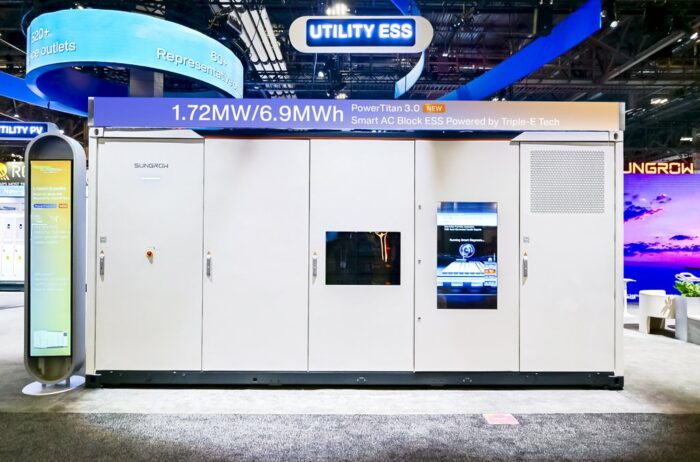

We wrote about Sungrow in more depth here, but Sungrow used RE+ 2025 to highlight its PowerTitan 3.0 energy storage system. Each 20-foot ISO container packs 6.9 MWh of capacity using the industry’s first mass-produced 661 Ah stacking LFP cells. With a rated cycle life of 12,500, the system is designed for 2–8 hour applications and a lower lifetime Levelized Cost of Storage.
On the power side, Sungrow introduced a 430 kVA liquid-cooled SiC PCS with 99.3% maximum efficiency and 93.6% round-trip efficiency at four hours (92% including auxiliary load). A five-level state-of-charge balancing system—from cell to block—maximizes usable capacity, while a back-to-back container layout trims footprint by 21% over the previous generation.
Thermal management uses a combination of liquid cooling and optimized airflow to reduce auxiliary power draw and extend system life. Safety is addressed with 11 layers of protection, from cell over-voltage monitoring to AC fusing, and the company’s ArcDefender technology to limit arcing risk. The entire system ships UL9540-certified for faster deployment.
The PowerTitan 3.0 embeds Sungrow’s Stem-Cell Grid-Forming Tech 2.0, supporting seamless transitions between grid-following and grid-forming, 20-millisecond response, and black-start capability at gigawatt scale. This functionality is particularly relevant for data centers, where massive load swings can destabilize conventional generators.
As Rich Law, senior engineer for Sungrow’s ESS Technical Solutions team, explained: “The biggest advantage of liquid cooling is just the stability of the system. Keeping the temperature range of the batteries as consistent as possible allows the batteries to degrade evenly together. Because, in reality, in energy storage, the weakest point is the weakest cell in the system.”
Viridi joins Schneider Electric’s resilience initiative

Schneider Electric’s Accelerating Resilient Infrastructure Initiative, launched Sept. 18 with partners like Microsoft and AlphaStruxure, includes Viridi Energy as a key ecosystem player. Viridi promotes “fail-safe battery energy storage systems” designed to prevent thermal runaway at the cell level. Viridi’s enclosures use proprietary anti-propagation technology engineered to stop fire spread and maintain system integrity during abnormal thermal events. The company also builds its systems in the U.S.
“This partnership marks a pivotal step forward in defining how resilient microgrids are designed and deployed,” said Jon M. Williams, CEO of Viridi. “By combining Schneider’s integration expertise with Viridi’s safest-in-class systems, we can deliver solutions that meet stringent safety standards without compromising performance.”
The partners said the Accelerating Resilient Infrastructure Initiative is designed to unlock $7.5 billion in financing and streamline the deployment of resilient, community-based energy systems while current federal incentives remain available. The model connects developers, technology providers, and financiers in a single platform for scoping, building, and operating projects such as microgrids, solar + storage systems, and EV charging infrastructure.
Wärtsilä: First-of-its-kind safety validation
Wärtsilä Energy Storage announced a milestone in BESS fire safety with large-scale tests of its Active Ignition Mitigation System (AIMS) inside its Quantum2 enclosures. Unlike traditional containment systems that wait for gases to accumulate before venting or burning off, AIMS uses controlled sparker systems to ignite flammable gases the moment they are detected—well before they can build up to dangerous levels.
In July, Wärtsilä ran three separate “worst-case” thermal runaway simulations in the U.S., releasing flammable gas blends equivalent to UL 9540A test conditions. Each trial was observed by a major U.S. utility, a fire alarm vendor, and independent consultants. Across all three, AIMS prevented uncontrolled deflagrations, kept structural deformation at zero, and left the container fully intact.
“This test is a first-of-its-kind in the industry,” said Tamara De Gruyter, Wärtsilä EVP. “We’re not just rethinking how storage systems are built—we’re collaborating with first responders and customers to raise the bar for safety.”
The company argues that AIMS represents a paradigm shift: moving from reactive fire mitigation to proactive explosion prevention. By deliberately and safely igniting trace gases, AIMS reduces risks to firefighters, customers, and communities, while protecting system integrity and uptime.
Delta: Data center-ready microgrids
Delta used RE+ 2025 to showcase its Data Center Microgrid Solution, designed to deliver <4ms response time and ±2% voltage regulation under the heavy and variable workloads of AI-driven data centers. The system uses Virtual Synchronous Generator (VSG)-based synchronization to keep multiple power sources in lockstep, ensuring seamless transitions on- and off-grid.
The solution integrates renewables, batteries, and gensets with real-time controls and black-start capability. By modeling small-signal and transient responses, Delta says it can maintain stable microgrid operation even under grid connection delays and power quality fluctuations. Its string PCS for BESS, built on 215 kW modules, supports 2–5 MW configurations at 1500 V DC input, with CEC efficiencies above 98.3%.
Fluence: Smartstack manufacturing begins

Fluence has begun manufacturing Smartstack, its most advanced storage platform to date. Smartstack is an AC-based, modular enclosure system engineered to deliver ~30% higher energy density than leading peers, unlocking more megawatt-hours on constrained sites.
Manufacturing is underway at a fully automated facility in Vietnam with annual capacity projected at 35 GWh. Automation enables higher precision, lower labor costs, and tighter quality control, which Fluence says are critical to scaling deployments at utility scale.
Smartstack’s modular design splits large systems into smaller, shippable units that ease logistics, lower installation complexity, and improve site density. Available with long-term performance guarantees, Smartstack offers up to 99% availability, the industry’s first Dispatchable Energy Guarantee, and efficiency and capacity guarantees extending to 25 years.
For developers, these guarantees reduce financial risk and increase bankability, while the high density makes previously unviable sites workable. “The start of Smartstack manufacturing is the tangible realization of our commitment to innovation,” said Peter Williams, Fluence’s Chief Product and Supply Chain Officer.
NeoVolta: Entering the C&I storage market
NeoVolta, long known for residential storage, is stepping into the commercial and industrial segment with its new 250 kW / 430 kWh BESS, set for release in Q4 2025.
The system is modular and scalable, allowing integrators to stack units for larger commercial deployments. It comes with integrated controls for demand management and time-of-use arbitrage—capabilities increasingly critical for businesses facing rising demand charges. The unit is compatible with solar, generator, and grid-tied configurations, making it suitable for both backup power and grid services participation.
“Expanding into the C&I market is a natural evolution,” said CEO Ardes Johnson. “Commercial customers want the same safety, reliability, and flexibility that installers already know us for in the residential market.”
The 250 kW / 430 kWh format positions NeoVolta to compete in the mid-market C&I space, where projects often range from 500 kW to 5 MW. By offering modularity, NeoVolta can address both small commercial sites and larger aggregated projects. Distribution will run through existing channels with added direct sales for large projects.




Comments are closed here.